Remote Vs Local Mail Exchange in cPanel, email routing settings determine how incoming emails are handled for a domain. The two primary routing options are Remote Mail Exchanger and Local Mail Exchanger.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between these two settings:
Remote Mail Exchanger
When you select Remote Mail Exchanger:
- Email Delivery: Emails for the domain are routed to an external mail server, not the server where cPanel is hosted.
- Use Case: This is typically used when your email service is hosted by a third-party provider, such as Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft 365, or any other external mail server.
- DNS Configuration: The domain’s MX (Mail Exchange) records must point to the external mail server. cPanel will prioritize the MX records listed for the domain.
- Local Server: The local server (where cPanel is installed) will not attempt to deliver or store emails for the domain. It simply forwards them to the designated remote mail server.

Local Mail Exchanger
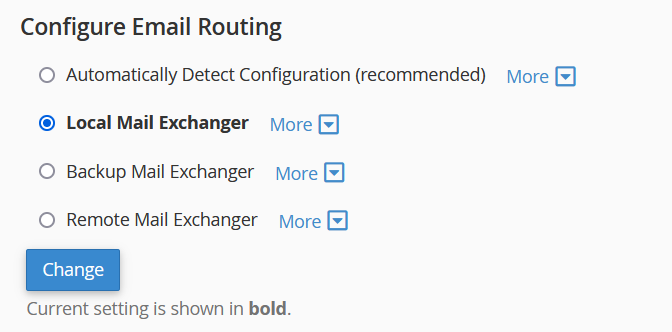
When you select Local Mail Exchanger:
- Email Delivery: Emails for the domain are routed to the local server where cPanel is hosted.
- Use Case: This is typically used when you want to handle and store emails directly on the cPanel server.
- DNS Configuration: The domain’s MX records should point to the local server’s IP address. cPanel recognizes itself as the primary mail server for the domain.
- Local Server: The local server handles the delivery, processing, and storage of incoming emails.
Key Differences between Remote Vs Local Mail Exchange in cPanel
- Destination: Remote Mail Exchanger routes emails to an external mail server, while Local Mail Exchanger routes them to the local cPanel server.
- Configuration: Remote Mail Exchanger requires MX records to point to an external server, whereas Local Mail Exchanger requires MX records to point to the local server.
- Control and Management: With Remote Mail Exchanger, email management (such as spam filtering, mailbox storage, etc.) is handled by the external provider. With Local Mail Exchanger, between Remote Vs Local Mail Exchange in cPanel are managed within the cPanel environment.
- Use Case: Choose Remote for third-party email services and Local for managing emails within your cPanel server.
When to Use Each Option
Remote Vs Local Mail Exchange in cPanel
- Remote Mail Exchanger: Use this if you prefer or are required to use an external email service for handling your domain’s email. This is common for businesses using professional email services like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365.
- Local Mail Exchanger: Use this if you want to keep email management and storage on the same server that hosts your website or if you prefer to manage your own email infrastructure.
How to Configure in cPanel
To configure these settings in cPanel:
- Log in to cPanel.

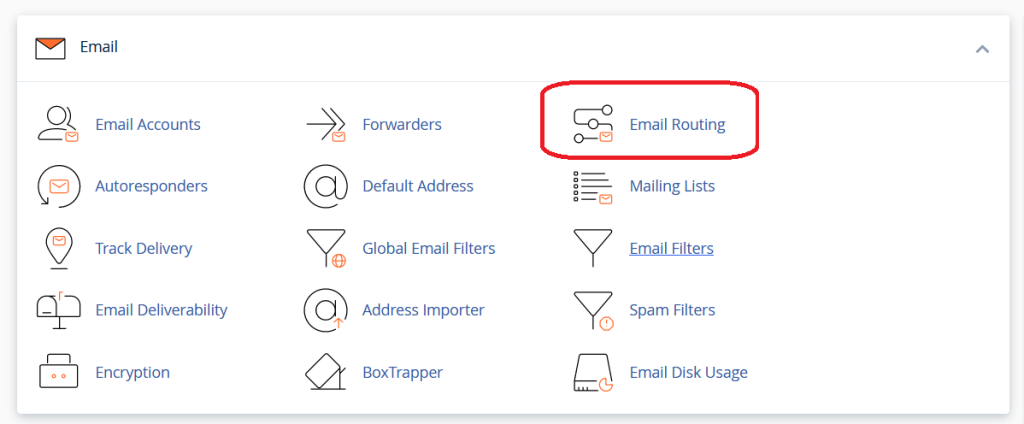
- Navigate to Email Routing: Look for the “Email Routing” option under the “Email” section.
- Select Domain: Choose the domain for which you want to configure email routing.

- Choose Routing Option: Select either “Remote Mail Exchanger” or “Local Mail Exchanger”.
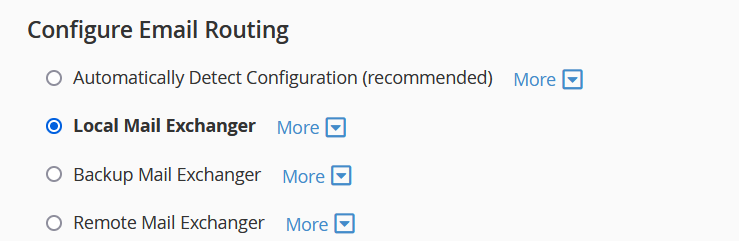
- Save Changes: Ensure that your MX records are correctly configured according to your selection.
By understanding between Remote Vs Local Mail Exchange in cPanel options, you can ensure that your email is routed correctly according to your organizational needs and infrastructure.

